Virtualization has become the cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, reshaping how businesses manage and utilize their servers. It’s a transformative technology offering numerous benefits regarding resource efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Introduction to Server Virtualization
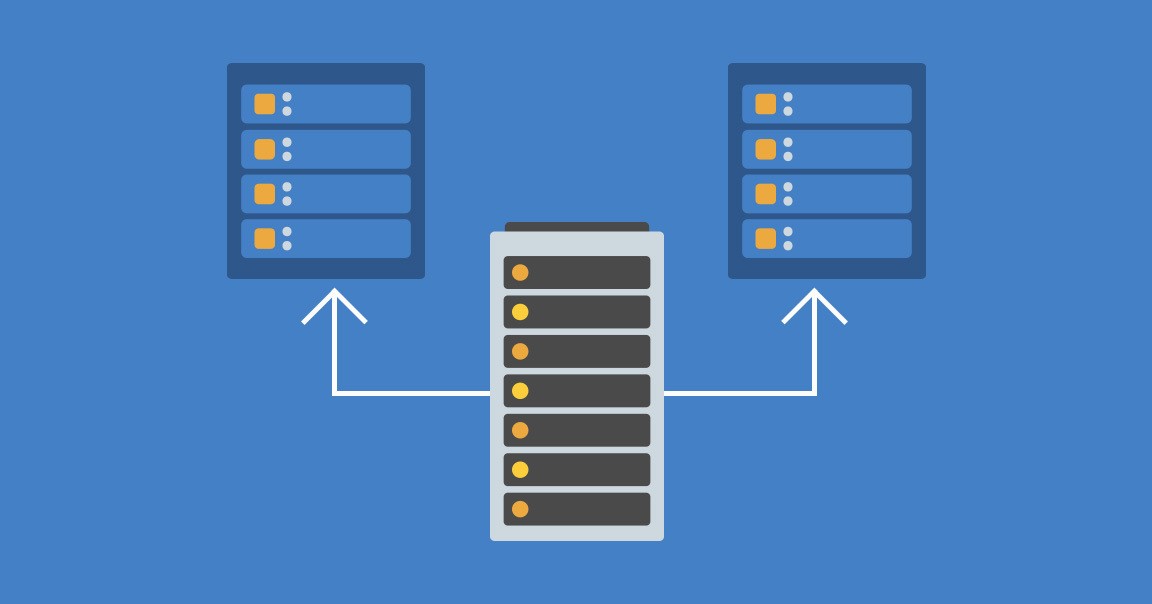
Server virtualization is dividing a physical server into multiple isolated environments using virtualization software. It allows one server to run various operating systems or applications, optimizing resources and maximizing efficiency. This technology is pivotal in today’s digital landscape due to its ability to reduce hardware costs, streamline operations, and enhance overall system performance.
How Server Virtualization Works?
Server virtualization functions as an innovative technology that transforms the operation of a physical server into multiple virtual servers. At its core, this process is made possible through a critical component called a hypervisor. The hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), is pivotal in managing and allocating the physical server’s resources effectively.
The primary function of the hypervisor is to create and manage these virtual machines (VMs) by dividing the physical server’s resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, into multiple isolated environments. These VMs act as independent entities, each capable of running its operating system and applications.
The process typically involves the following steps:
Hypervisor Installation:
Initially, the hypervisor software is installed on the physical server. It acts as an intermediary layer between the underlying hardware and the virtual machines.
Resource Allocation:
The hypervisor allocates the available resources, such as CPU cycles, memory, and storage, among the virtual machines based on predefined settings or dynamic allocation requirements.
Isolation of Environments:
Each VM is isolated from the others, ensuring that they operate independently without interfering with one another. This isolation ensures that if one virtual machine experiences issues or requires maintenance, it does not impact the performance of other VMs.
Operating System Installation:
Once the resources are allocated, each VM is loaded with its operating system and applications, making it function as an individual server within the larger physical server.
Resource Management:
The hypervisor continuously monitors and manages the resources, allowing for the dynamic adjustment of resource allocation per the changing demands of the VMs.
The hypervisor manages the communication between the VMs and the underlying physical hardware. It ensures that the resources are efficiently utilized and that the performance of each VM is optimized.
Furthermore, by consolidating multiple virtual servers on one physical server, server virtualization facilitates better resource utilization, reduced hardware costs, and more efficient IT infrastructure management. This not only leads to cost savings but also improves scalability and flexibility in managing workloads, catering to the dynamic needs of businesses.
In essence, server virtualization works by leveraging a hypervisor to divide a physical server into multiple isolated environments, allowing for enhanced resource utilization, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in managing IT infrastructure.
Advantages of Server Virtualization
Server virtualization offers several advantages, transforming how businesses manage their IT infrastructure and resources. Here are five key benefits:
Cost Savings:
Server virtualization leads to significant cost reductions by consolidating multiple virtual servers onto a single physical server. This consolidation minimizes the need for multiple hardware units, decreasing hardware acquisition, maintenance, and operational costs. Companies benefit from lower energy consumption and reduced physical space requirements, leading to substantial savings in both capital and operating expenditures.
Enhanced Resource Utilization:
By dividing a physical server into multiple virtual machines, server virtualization optimized resource utilization. The technology allows better allocation of CPU, memory, and storage, ensuring that resources are efficiently utilized across multiple workloads. This improved efficiency results in increased productivity and better performance from existing hardware, maximizing the use of available resources.
Scalability and Flexibility:
Virtualization provides businesses with unparalleled scalability and flexibility. It enables the rapid deployment of additional virtual machines to accommodate increased workloads or changing business needs without procuring new physical hardware. This flexibility allows for quick and seamless adjustments, ensuring businesses adapt swiftly to evolving demands or fluctuating workloads.
Simplified Management and Maintenance:
Server virtualization streamlines the management and maintenance of IT infrastructure. Through centralized management tools, administrators can efficiently monitor and control multiple virtual machines from a single interface. Tasks like backups, updates, and resource allocation become more streamlined, reducing administrative overhead and simplifying routine maintenance operations.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery:
Virtualization technology offers enhanced high availability and robust disaster recovery capabilities. Through features like live migration and redundancy, virtual machines can be moved between physical servers without disruption. This ability to move workloads ensures continuous operations, minimizes downtime, and facilitates efficient disaster recovery strategies, enhancing the overall reliability of IT systems.
These advantages demonstrate the transformative impact of server virtualization, providing businesses with cost efficiencies, optimized resource utilization, flexibility, simplified management, and improved system resilience.
Types of Server Virtualization
Server virtualization encompasses several types, each employing distinct approaches to create and manage virtual environments. Here are three primary types of server virtualization:
Hardware Virtualization:
Hardware virtualization involves using a hypervisor to create multiple virtual machines on a physical server. Each virtual machine runs its operating system and applications, allowing different operating systems to coexist on the same hardware simultaneously. This method provides a high level of isolation and security between virtual machines.
OS-Level Virtualization:
OS-level virtualization, or container-based virtualization, divides the host operating system into containers. These containers share the same OS kernel but operate independently, hosting different applications or services. It’s efficient, lightweight, and suitable for scenarios requiring multiple instances of the same operating system.
Paravirtualization:
Paravirtualization modifies the guest operating system to be aware of the virtualized environment. This enables more efficient communication and interaction between the guest OS and the hypervisor, improving performance compared to traditional hardware virtualization methods.
Citrix Hypervisor: Streamlining Virtualization Solutions
Citrix Hypervisor, previously known as Citrix XenServer, is a powerful and comprehensive server virtualization platform designed to deliver high-performance, efficient business virtualization solutions. As a leading virtualization management platform, Citrix Hypervisor offers a range of features and functionalities tailored to optimize the management of virtual infrastructure.
Key Features and Capabilities
1. High Performance Virtualization:
Citrix Hypervisor provides robust performance capabilities, supporting various workloads and applications. It offers efficient resource management, allowing businesses to optimize their server resources while ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
2. Enhanced Security and Isolation:
Security is a priority in virtualized environments. Citrix Hypervisor ensures strong isolation between virtual machines, reducing vulnerabilities and providing secure environments for running diverse workloads.
3. Centralized Management Console:
The platform boasts a user-friendly centralized management console, offering a streamlined interface for administrators to manage and monitor virtual machines, resources, and configurations across the infrastructure.
4. High Availability and Disaster Recovery:
Citrix Hypervisor includes features for high availability and disaster recovery, enabling seamless failover and recovery procedures. Live migration capabilities allow virtual machines to be moved between hosts without service interruption, ensuring continuous operations.
5. Integration and Compatibility:
It integrates well with other Citrix products and various third-party applications, making it a versatile choice for businesses looking to adopt virtualization within their existing ecosystem.
Use Cases
Citrix Hypervisor is utilized in various industry verticals and business sizes. Its versatility makes it suitable for diverse use cases, including:
Enterprise Data Centers:
Offering flexibility and scalability for large-scale data center environments.
Development and Testing Environments:
Providing a reliable and cost-effective platform for testing new applications and services.
Desktop Virtualization (VDI):
Enabling efficient delivery of virtual desktops for remote and distributed workforces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, server virtualization is a game-changer in modern IT landscapes, offering unparalleled efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Its continual evolution promises a future where businesses can optimize their resources more effectively.
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of server virtualization?
Server virtualization primarily aims to optimize server resources, reduce hardware costs, and enhance operational efficiency by creating multiple isolated environments on a single physical server.
What are the key challenges associated with server virtualization?
Challenges include security concerns, performance issues, and compatibility challenges that must be carefully addressed to ensure a seamless experience.
How does server virtualization contribute to cybersecurity?
By implementing robust cybersecurity measures within a virtualized environment, sensitive data can be safeguarded, ensuring the system’s integrity.
What are the future trends in server virtualization?
Future trends involve the fusion of edge computing with virtualization and the integration of AI to optimize resource allocation, among other advancements.
How does server virtualization differ from traditional infrastructure?
Server virtualization offers benefits such as enhanced resource utilization and scalability, whereas traditional infrastructure might have limitations in these areas.